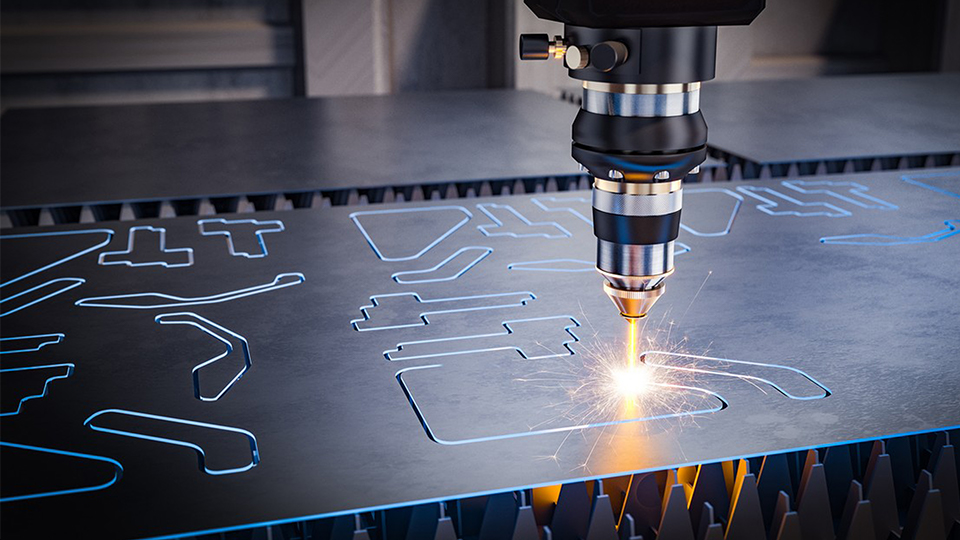
The laser cutter is a cutting machine that enables precise and complex cutting of various materials. It uses a high-powered laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize the material, thereby achieving precise cutting of the material into the desired shape.
This article will discuss what laser cutting is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and its applications.
What is a laser cutter?
Laser cutting is one of the thermal cutting processes. It employs a focused high-energy laser beam to irradiate and heat the blank piece and makes the heated materials quickly melt or vaporize, and then shapes them into the desired geometry by movement of the beam.
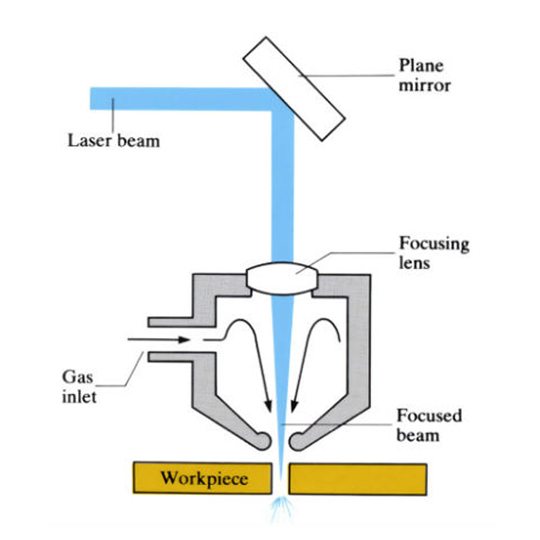
An almost parallel laser beam is generated in the laser source; a mirror is used to direct the laser beam towards the cutting head; and a lens is used at the cutting head to focus the laser beam. The focused, high-energy laser beam shines on the surface of the workpiece, rapidly heating the workpiece and melting the material. Auxiliary gas is used to protect and cool the focusing lens and clear molten metal.
Types of laser cutter
Laser cutting machines can divided into 3 types by the lasers they employ:
- Fiber laser cutter: The fiber laser machine converts electricity into light through the SPI/IPG laser, and then irradiates the high-energy laser beam onto the surface of the blank piece through the cutting head, vaporizing the irradiated material instantly. A fiber laser cutter is mainly used for metals like stainless steel, carbon steel and aluminum alloys.
- CO2 laser cutter: The CO2 laser cutter uses CO2-based gas to generate a laser beam to cut or engrave materials. In this cutting process, auxiliary gas such as oxygen or argon is used to increase cutting speed and clean the material surface. The CO2 laser cutter is mainly used for non-metal materials like plastics and glasses.
- Crystal laser cutter: Crystal laser cutting machines use Nd: YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) and Nd: YVO (neodymium-doped yttrium vanadate), usually the former is more commonly used, to generate laser beams to cut and engrave materials.
Summary of the different laser cutter
| Factors | Fiber laser cutter | CO2 laser cutter | Crystal laser cutter |
| Wavelength(μm) | 1.06 | 10.6 | 1.06 |
| Spot diameter(mm) | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.3 |
| Pump source | Diode laser | Gas discharge | Lamp, diode laser |
| Energy conversion | 10% | 25% | 3% |
| Materials | Metals, especially thin plate | Non-metals, acrylic, glass, paper, textiles, plastics | Metals, plastics, ceramics |
How does a laser cutter work?
The Laser cutter uses a high-energy laser beam to molten or evaporate the material, thereby cutting and shaping the parts. Its workflow can be summarized into 4 parts:
- Generate a laser: A laser beam is generated by a laser generator, this is a process like turning on a flashlight.
- Enables the laser to be focused: The laser light passes through a series of optical elements, such as lenses and mirrors, which focus it onto a very small spot with extremely high energy density.
- Cut the material: The focused laser beam hits the surface of the material, which is melted or vaporized by the laser, creating a small hole. The laser cutter moves along a planned path to shape the desired geometry.
- Blow away the extra material: The laser cutter often uses something called an “auxiliary gas”, such as oxygen or nitrogen, to blow away any extra material in the cutting area, keeping it clean and helping to speed up the cutting process.
Suitable Materials
The compatibility of a material with laser cutting methods depends on its physical and chemical properties. Materials with low reflectivity, thermal conductivity and chemical stability can be processed using laser cutting. The common types of materials for laser cutting include metals, plastics, and wood.
Metals
Metals are the common materials used in laser cutting. Since metal materials have a high absorption rate of laser beams, high-quality cutting results can be achieved. Laser cutting of metal materials has the advantages of fast speed, high precision, and small heat-affected zone, and is widely used in automobile manufacturing, machinery manufacturing, aerospace and other fields. the common metals for laser cutting include:
- Aluminum: Such as 5052, 5074.
- Stainless steel: Such as 304, 316L
- Copper: such as C110
- Carbon steel
- Titanium

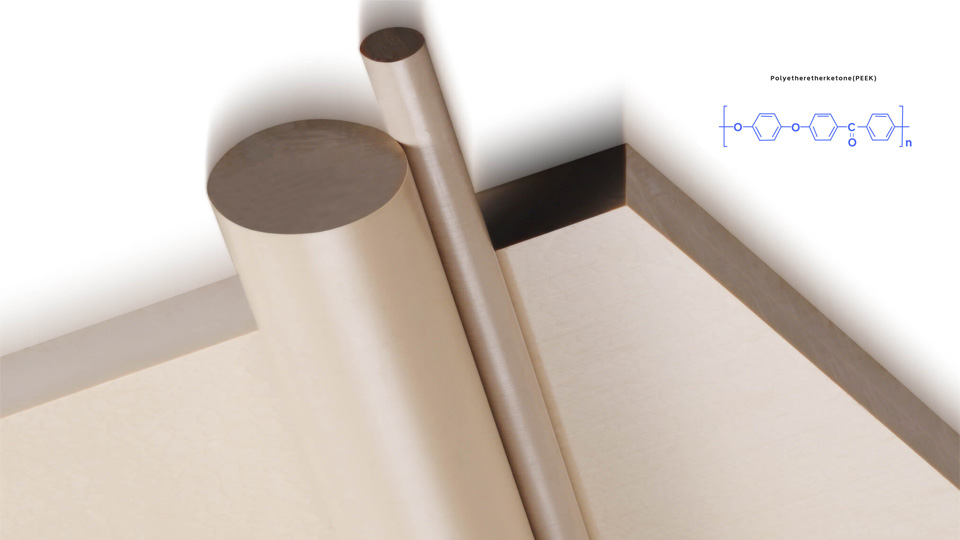
Plastics
Not all plastics are suitable for laser cutting processes. The plastic needs to be able to absorb laser energy without excessive melting or harmful emissions. The common plastics for laser cutting include:
- Acrylic
- PEEK
- Nylon
- PE

Wood
Laser cutting is ideal for prototyping with wood and creating complex furniture parts and artistic designs. It has a very small kerf (kerf width).

Different materials react differently to laser cutting, and understanding the suitability of a material helps us choose the right cutting machine.
| Materials | Machine type | Power | Speed |
| Metals | CO2 laser cutter, High-power Fiber laser cutter | High | Medium |
| Plastics | CO2 laser cutter | Medium | Medium |
| Wood | CO2 laser cutter | Medium | Low |
Inappropriate materials
As mentioned above, some materials are difficult to use for laser cutting if they have all or one of the following characteristics, including high reflectivity, easy combustion, and toxic emissions. Some inappropriate materials include:
- Carbon fiber
- ABS
- PVC
- PTFE
- HDPE
- Fiberglass
- PC
- PP
Advantages
The advantages of laser cutting technology are obvious. Some of these advantages are discussed below:
High precision and accuracy
The accuracy of laser cutting depends not only on the laser itself but also on the accuracy of the motion system. Typical tolerances for laser cutting range from 0.003mm to 0.006mm, other cutting tools tolerance levels range from 1mm to 3 mm or even higher.
Modern high-end laser cutting machines use linear motors and optical scales to achieve a positioning accuracy of ±0.001mm in some cases.
Contact-free processing
Laser cutting is a contact-free process, which means there is no physical contact between the cutting tool and the material. This reduces wear on the cutting equipment and reduces the risk of contamination. The result is cleaner, with minimal material deformation. Due to its non-contact nature, laser cutting can process fragile or easily deformed materials.

Fast cutting speed
For example, with 2KW laser power, the cutting speed of 8mm thick carbon steel is 1.6m/min; the cutting speed of 2mm thick stainless steel is 3.5m/min, with a small heat-affected zone and minimal deformation.
Wide range of cutting materials
Compared with oxyacetylene cutting and plasma cutting, laser cutting can cut a variety of materials, including metals, non-metals, composite materials, leather, wood, fiber, etc. However, different materials have different laser cutting compatibility due to their thermophysical properties and laser absorption rates.
Disadvantage
Limited by the power of the laser and the size of the equipment, laser cutting can only cut small to medium thickness plates and tubes.
As the thickness of the material increases, the cutting speed decreases significantly.
Laser cutting equipment is expensive and requires a large one-time investment.
Applications
Since laser cutting has some unmatched advantages over other processes, such as high precision and short processing time, it is widely used in many industries.
Outdoor advertising
In the outdoor advertising industry, metal materials are frequently used. The use of laser cutting to process metal materials, and fonts can improve the visual effect of advertising materials, and improve the efficiency of production and processing so that the advertising company to increase profits.
Sheet metal fabrication
Due to its high level of flexibility, fast cutting speed, high cutting efficiency and short working cycle, laser cutting has made it highly favored in the sheet metal fabrication industry. Laser cutting requires no cutting force and there is no tool wear, in addition, the laser cutting slit is usually narrower and has a high level of automation.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, some accessories such as car doors and exhaust pipes will have some extra corners or burrs after processing. If they are processed manually or in traditional ways, it is difficult to ensure accuracy and efficiency. Using a laser cutting machine can easily solve the corner and burr problems in batches.
Kitchen utensils
In the kitchenware industry, range hoods and gas appliances usually use a large number of sheet metal panels. Traditional processing methods have the disadvantages of low work efficiency and high mold consumption, which not only consumes a lot of resources but also restricts the development of new products. Using laser cutting machines to process kitchenware products has extremely fast cutting speed and high cutting accuracy, which can improve processing efficiency and effectively improve the yield rate of range hoods and gas appliances.
Fitness equipment
Fitness equipment is mainly made of pipes. The use of laser cutting machines can quickly process pipes and complete the production and assembly of fitness equipment more quickly.
Laser cutting design guidelines
Keeping these design tips in mind can help you achieve better laser cutting results and save costs.
| Factors | Design tips |
| File Format | Use vector files such as DXF or DWG |
| Corner Fillets | No smaller than 1/2 material thickness |
| Hole-to-Hole Distance | At minimum 2X the material thickness |
| Hole to Hole Distance | At minimum 6X the material thickness |
| Relief Cuts | At minimum 1X the material thickness |
| Tab Thickness | At minimum 1X the material thickness |
| Hole-to-Edge Distance | At minimum 1X the material thickness |






