CNC ABS Machining Service
Our ABS machining service delivers precision prototypes with strength and toughness. Get instant quotes on ABS parts.

All drawings are secure and confidential.
What is ABS?
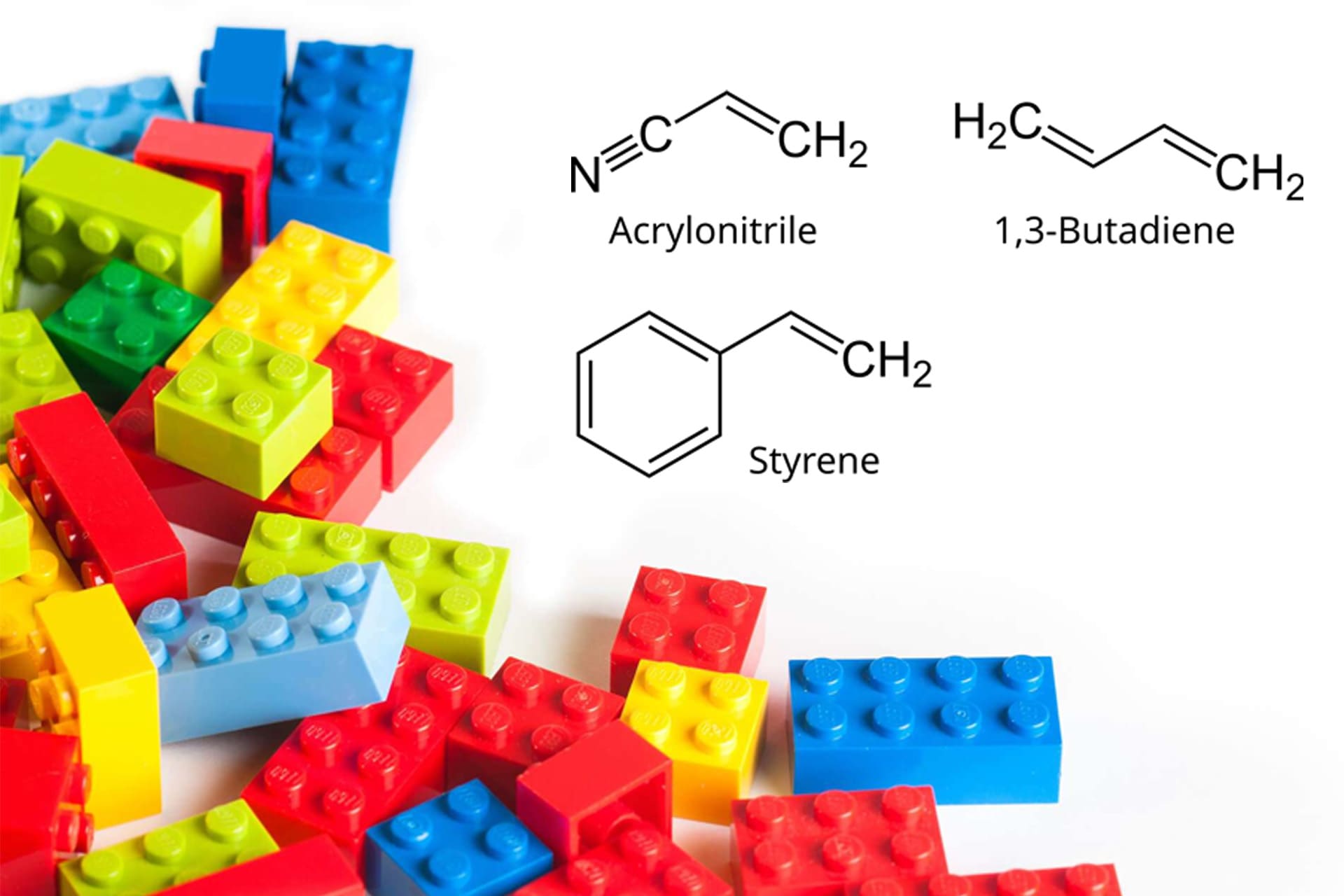
ABS is a ternary copolymer of acrylonitrile (A), butadiene (B), and styrene (S), making it one of the most widely used polymers.
- A (Acrylonitrile) provides chemical corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and a certain level of surface hardness. It is unaffected by water, inorganic acids, or food-grade acids and alkalis, and can be used in temperatures ranging from -50°C to +70°C. It offers excellent impact resistance at low temperatures and maintains good shape and dimensional stability when heated.
- B (Butadiene) contributes high elasticity and toughness. It delivers strong mechanical strength and rigidity, resists scratching, and provides high tensile strength, chemical resistance, wear resistance, and surface durability.
- S (Styrene) imparts the processing and molding characteristics of thermoplastics while enhancing electrical properties. It is easy to color and process, can be electroplated, and exhibits excellent chemical properties and electrical insulation.
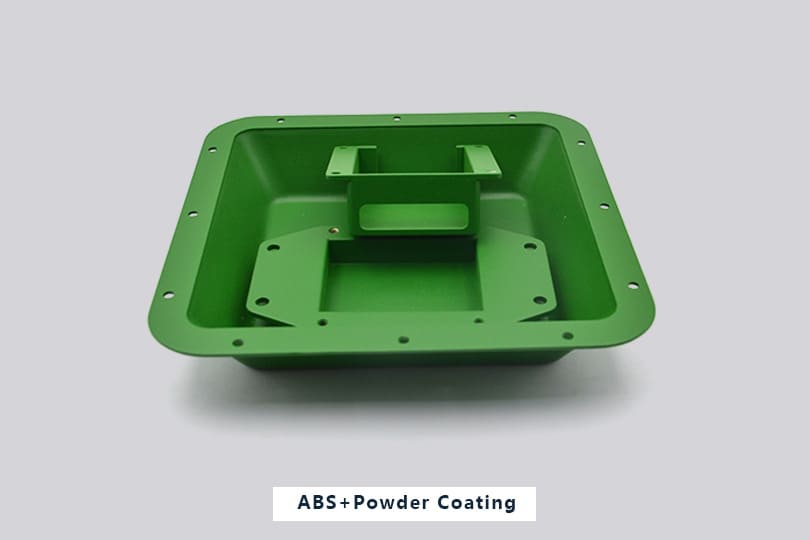
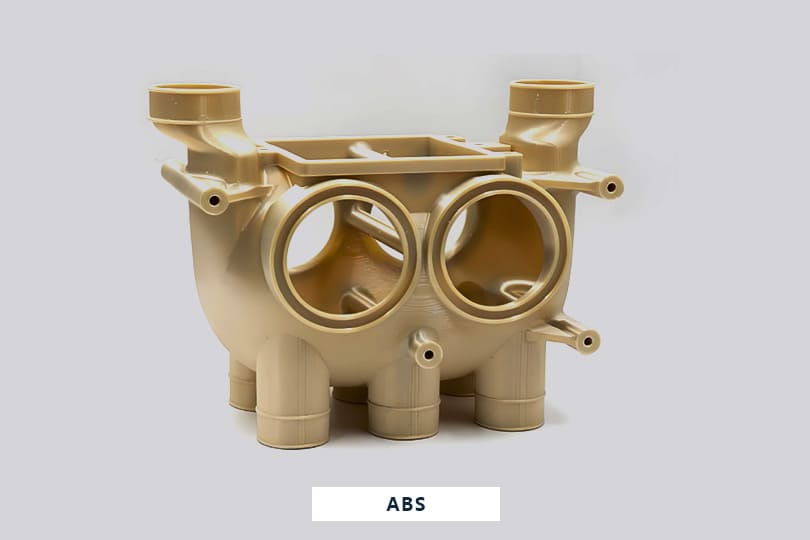
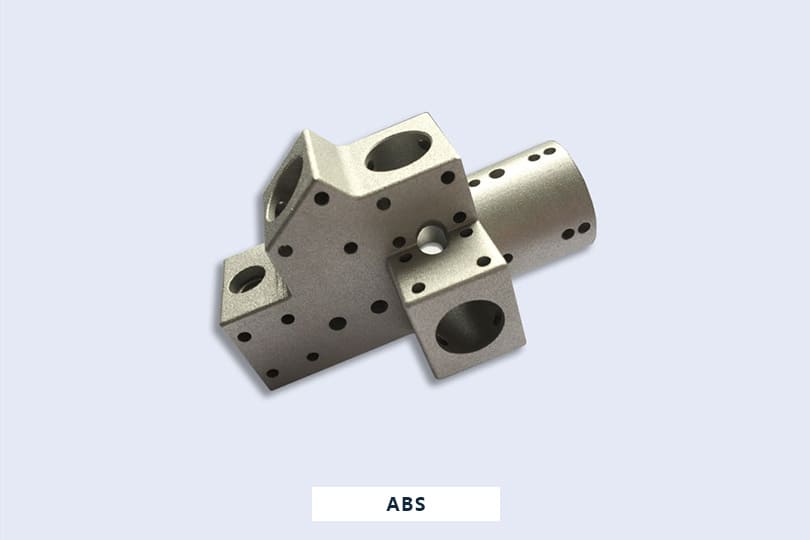
Gallery of ABS Machined Parts
Here are some of ABS parts we produced for our valued customers all over the world.
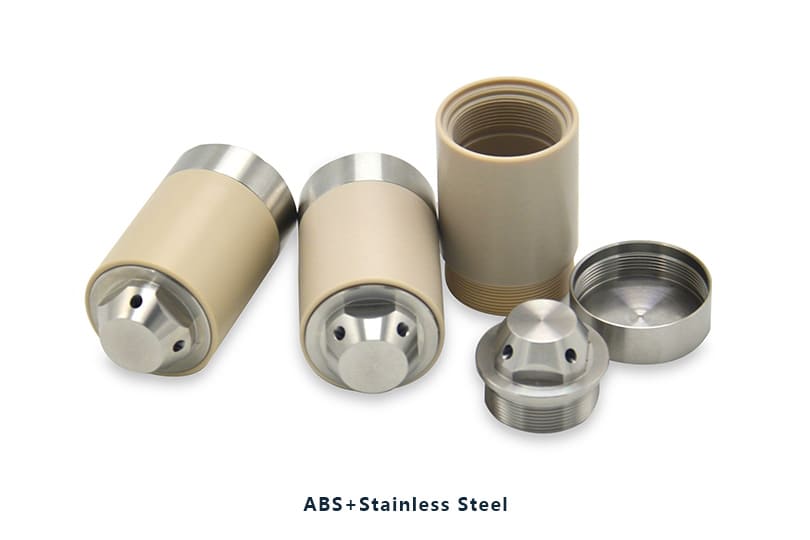
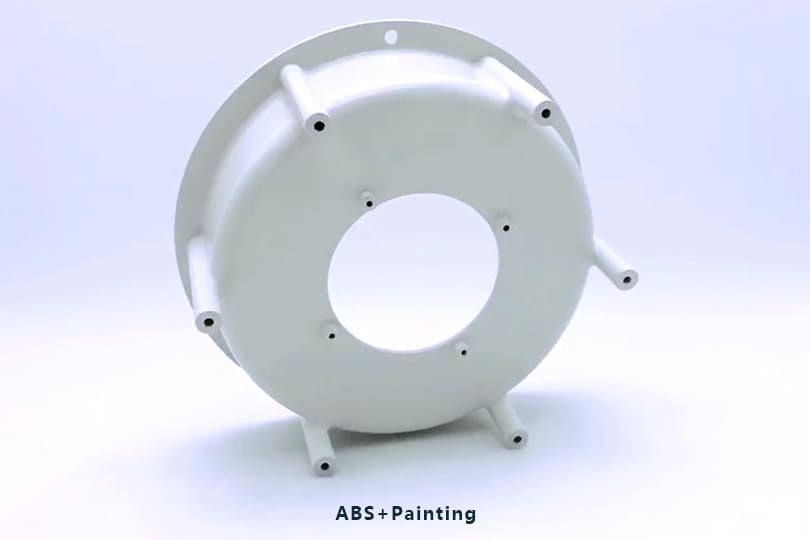





Advantages of ABS in Machining
Advantages
- High impact strength, capable of use even at low temperatures, with excellent wear resistance and dimensional stability.
- Excellent electrical insulation that is unaffected by temperature, humidity, and frequency.
- ABS plastic has excellent resistance to corrosion from acids, alkalis, salts, and other chemical substances.
Notes
- ABS plastics are sensitive to UV light and tend to yellow and become brittle when exposed to sunlight for long periods, reducing their lifespan.
- Although ABS sheets have good heat resistance, they tend to soften or deform in high-temperature environments.
- ABS sheets are sensitive to some organic solvents and can easily dissolve or deform, so it is important to avoid contact with solvents.
ABS Material Properties
Tensile Strength |
Elongation |
Hardness |
Melting Point |
Heat Deflection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
40 MPa |
25% |
90-100 HRB |
267 °C |
97.4 ℃ |
ABS Machining Processes
In the processing of ABS plastic, raw materials are typically in the form of granules or powder and can be processed using various molding techniques, including injection molding, extrusion, and 3D printing. Injection molding is the most common method for ABS processing, and it is ideal for producing parts with complex geometries and large-scale production. Extrusion is often used to manufacture ABS pipes, sheets, or profiles.
For parts with tight tolerances, precision CNC machining is an important complementary process in ABS machining. When machining ABS plastic, it is recommended to use machine-grade ABS materials, which offer higher density and consistency, reducing deformation or surface defects during processing.

- Always use machine-grade ABS plastics when milling, turning, or drilling to ensure good chip formation and a superior surface finish.
- Use a non-aromatic, water-soluble coolant optimized for machining plastic parts, coolants can be applied as a jet of pressurized gas, a continuous mist, or a flowing liquid.
- Put ABS plastic in a heat treatment oven prior to machining, the material can be slowly heated, held at the annealing temperature, then slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses.
